Heart Surgery :
In heart surgery, surgeons perform surgeries through small incisions in the right side of the chest section
Several types of cardiac procedures may be performed, including:
Aortic valve replacement
Tricuspid valve repair and replacement
Mitral valve repair and replacement
Atrioventricular septal defect repair surgery
Maze surgery to treat atrial fibrillation
Fixed atrial septal defect
Coronary artery surgery
Robotic cardiac surgery:
A robotic arm is used in place of the surgeon’s hands and surgery is very accurate here
And work on the process is done through robot control devices through which the heart is seen in a 3D view and is high definition on the screen.
Other surgeons change surgical instruments connected to auxiliary robotic arms at the operating table.
Thoracoscopy surgery:
A small opening is made through the chest, and the surgeon inserts a long tube through it. It contains a small, high-definition camera. The surgeon uses thin, long tools that are inserted through small cracks between the ribs.
Cardiac catheterization :
Cardiac catheters are usually performed when the patient is awake and under the influence of local anesthesia, either when performing excision or valve repairs, the patient is fully anesthetized.
During the operation, a tube is inserted into your arm and is used to provide the body with the additional drugs you need during the operation.
The supervising doctor can clean the site from which the catheter will be inserted from the hair before it is inserted into the artery, and the patient will be provided with a full anesthetic injection to numb the area, and the patient may feel a slight delay or some slight pain in that.
After the anesthesia takes effect, a cut is made to reach the artery, and the surgeon inserts a sheath or tiny, very thin plastic scales so that the doctor can insert the catheter.
Some common uses for catheterization:
Coronary angiography: Here the arteries leading to the heart are examined and verified, and a dye is injected here through the catheter and X-ray images are taken of the arteries of the heart. Coronary vessels are visualized and the catheter is placed through the arterial thigh or via the wrist.
Right catheterization: Here is a test to verify that blood pressure and that it is flowing in the correct form of the heart. The catheter contains sensors that measure the pressure and blood flow in the heart.
Heart biopsy: The doctor takes a biopsy of the heart tissue and put a catheter into a vein or sometimes in a vein of the thigh and a specific catheter is used to form a biopsy or a sample of the heart tissue.
Balloon angioplasty, with or without stents: In this process a narrowed artery or an artery within the heart is enlarged and is done by inserting a catheter through the wrist or thigh.
A catheter is attached through the arteries to the narrow artery, after which a balloon is connected through the catheter and inserted into it. This balloon is inflated to open the narrow area in the artery and the doctor places a stent that is a mesh fascia in the narrow part to help the artery to keep it open.
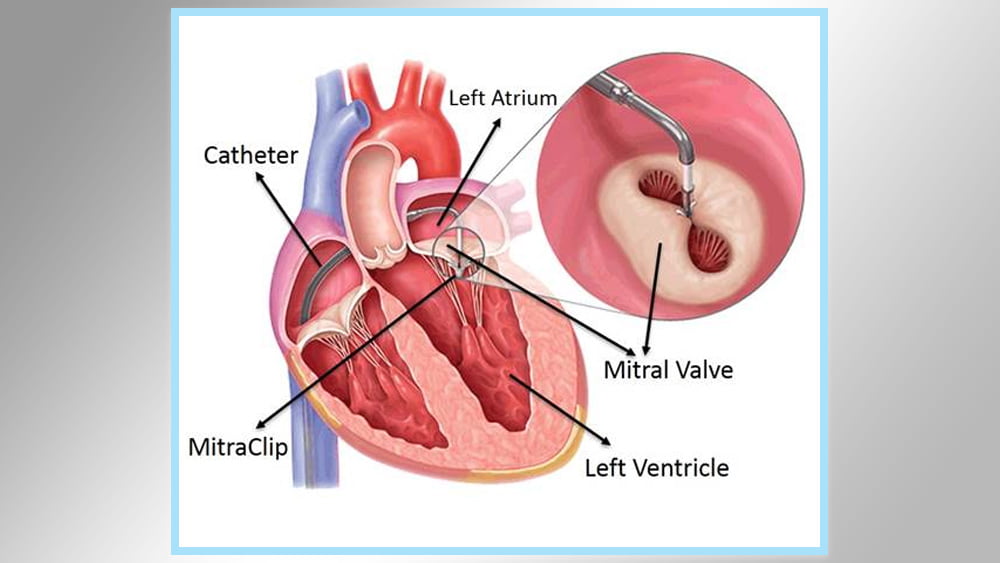
Correcting heart defects: This process is done to close a hole in the heart, for example, a perforation of the atrial septum or a passive oval hole. A catheter is inserted through the thigh and neck artery to block the hole. There are cases such as leaking of the heart valve. Here a clip or plug can be used to prevent leakage
Balloon valve valve surgery: This procedure is performed to expand the heart valves if the valves are weak and the location and position of the catheter depends on the specific heart valve problem in the patient.
We connect the catheter through the valve and inflate the balloon to open the valve easily. The patient may feel some pressure when inserting the catheter, but also he will feel comfortable after the balloon is inflated to expand.
Open heart surgery:
We resort to performing an open heart operation in the following cases:
Restoration and replacement of heart valves that allow blood to flow into the heart.
Restoration and repair of damaged areas of the heart.
A pacemaker implanted.
Replacing the heart with another from a donor.
How is an open heart operation performed?
Usually the open heart process takes 3 to 6 hours.
During the process:
During the operation a general anesthesia is made to the patient during the procedure so that he does not feel pain.
The surgeon makes a chest incision up to 20 to 25 cm
Some of the chest bones are spread to show the heart
After showing the heart, the patient is connected to a medical device that works to transfer blood separately from the heart.
The bones of the rib cage are closed and the incision in the chest is fixed.
Prepare for an open heart operation
It is necessary to tell the doctor about any medications the patient takes or any diseases he has.
A month before the operation, it is preferable to do the following:
Do not smoke and stop smoking
Stop taking blood-thinning medications such as aspirin and ibuprofen.
After the operation
After the procedure, upon the patient’s awakening, you will notice two tubes connected to the patient’s chest to drain fluid from the area around the heart.
Connecting tubes for feeding and one to the bladder to empty it.
There is also a special device to assess the condition of the heart after the operation and monitoring
Take care of the incision and wound
After the operation, if you see the wound recovered correctly, you can do a bath to wash the body, taking into account the following:
Water should not be delivered or directed to the wound area
Bath time should not exceed 10 minutes
Not to use hot water and be more warm
The wound should be monitored for infection without any of the following symptoms:
Large wound filtration
An opening in the wound
Redness around the wound area
High body temperature.
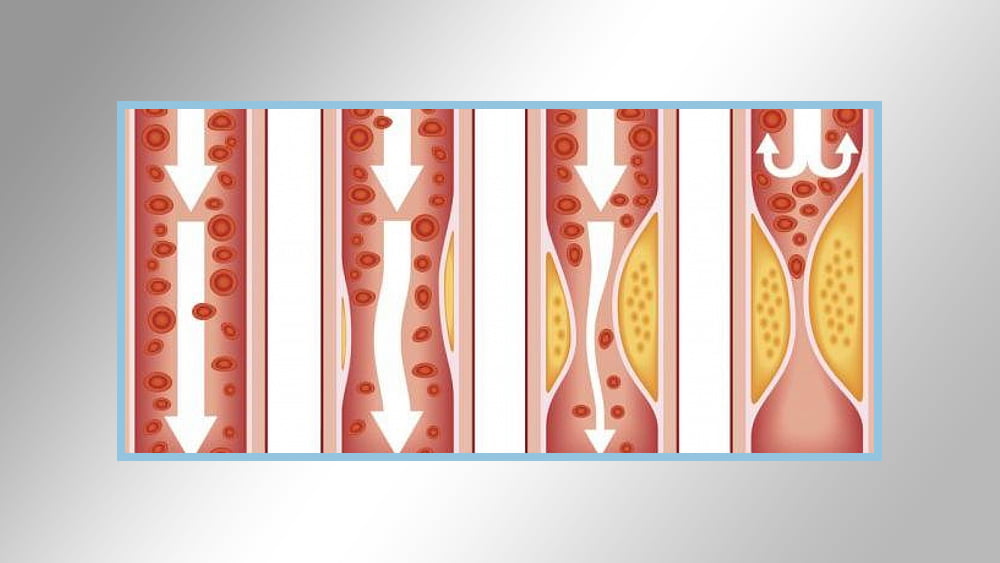
Arteriosclerosis:
Arteriosclerosis occurs when the blood vessels loaded with oxygen and food from the heart to the body are in a state of stiffness and thick, which prevents the blood from flowing to the organs and living tissues.
Atherosclerosis: It is a type of arteriosclerosis, and arteriosclerosis here indicates fat, cholesterol and other substances in the arterial wall, which prevent and hinder the payment of tears.
Symptoms
Symptoms of atherosclerosis are gradual and mild sclerosis is not usually associated with the appearance of any symptoms on the patient
Often the patient does not suffer from any symptoms when the arteriosclerosis is reached, except that it reaches an extreme stage that leads to dizziness and severe shortness of breath in a severe way, and it causes the delivery of oxygen to the organs and tissues in the body. It can become a clot and lead to obstruction of blood flow and may cause a heart attack or stroke.
Symptoms of moderate and severe atherosclerosis depend on the affected arteries:
If you have arteriosclerosis in the arteries of the heart: The patient may suffer from symptoms such as feeling chest pressure or angina.
In case you have arteriosclerosis in the arteries leading to the brain: the patient here suffers from numbness, weakness in the movement of the leg and arm, or even speech or distorted vision, as well as the loss of muscle capacity in the face and this is medically called a transient ischemic attack and can become a stroke if it does not occur Treat it directly.
If you have arteriosclerosis in the arteries in your arms or legs: This is related to the peripheral artery and has symptoms such as hair with leg pain when walking.
In the event that you suffer from atherosclerosis in the arteries leading to your kidneys: You may operate with pressure on the kidneys and also lead to kidney failure if treatment is not done.
Heart valves:
The function of the heart valves is the separation between the parts of the heart where we find at each outlet of the heart or a part we find a valve that does a job assigned to it, and the function of these valves is to monitor and maintain blood flow in a uniform direction and not allow reverse blood leakage, there are four main valves for the heart, namely:
Mitral valve: This valve is located at the tip of the left atrium exit of the heart and is separated from the left ventricle. This valve opens when systole and closes when it extends.
Tricuspid valve: This valve is at the exit of the right atrium and separates it from the right ventricle. It is opened upon contraction of the right atrium and closed when it extends.
Aortic valve: This valve is located at the exit of the left ventricle, and separates it from the aorta. This aortic valve opens when systole and closes when it is flat.
Pulmonary valve: This valve is located at the exit of the right ventricle, and separates it from the pulmonary artery. This pulmonary valve opens when the ventricle contracts, and closes when it contracts.
The blood circulation in the heart comes from all over the body through the veins and flows into the right atrium. The right ventricle contracts and after filling with blood, the pulmonary valve opens, and blood flows here towards the pulmonary artery.
Blood crosses the lungs to be supplied with oxygen that enters through the nose and oxygen returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins, and when the left atrium is filled with blood it begins to contract so the mitral valve opens and the blood crosses to the left ventricle and when the left ventricle is filled, the mitral valve is closed and the left ventricle is closed and opens Aortic valve to cross blood to the aorta through the left ventricle
An important note here is that the atria contract simultaneously, that is, the opening and closing of the mitral and tricuspid valves are at the same time, and the ventricles also contract at the same time exactly, that is, the aortic and pulmonary valves open and close with each other.
Pacemaker:
The purpose of implanting a pacemaker is to replace the normal organized cells present in the patient’s heart and these cells have the mission to generate a pacemaker signal for the heartbeat. These natural organized cells are based on sending electrical signals through the nerve fibers which causes the heart muscle to contract and in this way the heart performs its primary function of pumping Blood to and through the body.
Any problem in the normal organized cells present in the sinus node of the ear in the right atrium of the heart will lead to disturbances in the organization of the heart, for example: slow heart, a problem in the ventricular atrium, and others.
The pacemaker consists of a capsule and inside it contains a battery and an electrode through which the signals produced by the pacemaker pass through to the heart muscle cells.