Pelvic joint replacement:
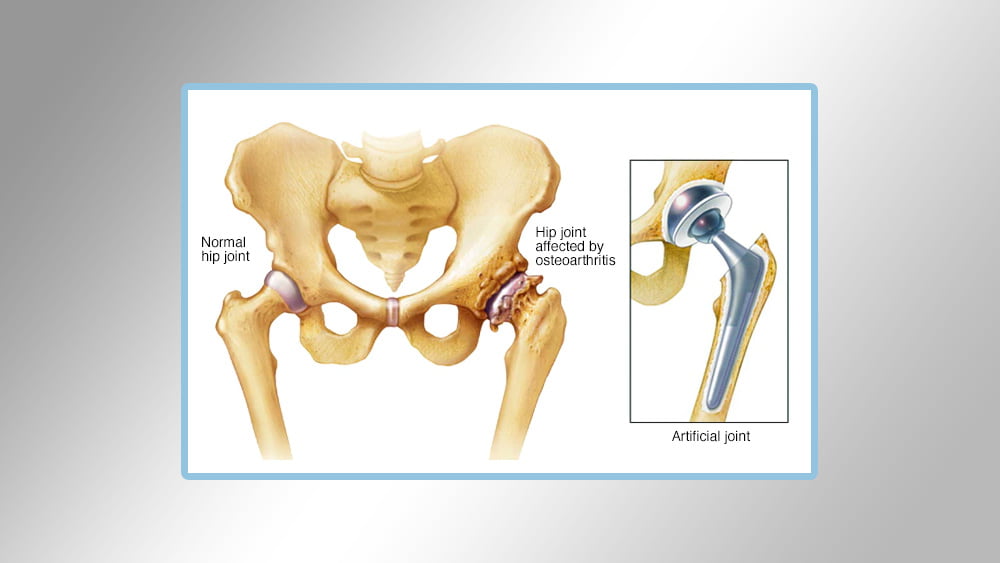
When replacing the pelvic joint, the doctor removes the damaged parts of the hip joint or pelvis, as it is called, and replaces parts that are usually made of metal, medical plastic, or very hard ceramic.
Conditions that can damage the pelvic joint, and that require pelvic joint replacement surgery include:
Osteoarthritis: It is an inflammation of the joints as a result of the rupture of the tissues of the joint and leads to the destruction of slippery cartilages covering the ends of the bone, which help the joints to move smoothly.
Rheumatoid arthritis: This inflammation is caused by hyper immune activity and is a type of inflammation that can lead to erosion of cartilage and bone, leading to destruction. Necrosis, if the blood does not reach the spherical part of the hip joint, the bone may be damaged and distorted.
You can also do hip replacement surgery if the patient has pain in the hip joint and is continuous despite taking painkillers.
– It increases or worsens with effort or walking.
The patient is affected by the hours of sleep.
Difficulty getting down or getting started.
Difficulty getting out of the sitting position.
Steps for surgery and hip replacement:
Make incisions from the front of the hip through the tissue.
Removing damaged and damaged cartilages and bones.
Cultivation of the artificial cavity at the base of the pelvic bone to be the place of the damaged cavity
Replacing the place of the round ball in the upper parts of the femur with an artificial pulley that is proportional to the femur
After the operation, the patient will be transferred to the recovery area for a few hours at the time of expiry of the anesthesia effect, and the patient will be monitored through the medical staff, blood pressure, alertness, the amount of pain, etc., and the patient’s needs for medication and treatment.
Knee joint replacement:
The most affected body is the knee joint due to its daily functions, and it may be subject to erosion for several reasons such as aging, calcium deficiency, etc. The patient may need an operation to replace the knee joint.
The knee joint can be treated by physical therapy physically or through medication, but when these attempts and treatments fail, the doctor will resort to a process to replace the joint. There are several types of knee joint changes, which are:
Total knee replacement: The femur and leg attached to the knee are replaced here and this type is the most common between operations.
Partial knee replacement: Here, a partial part of the knee is replaced, damaged, and replaced with another healthy part, caused by infections.
Patella replacement: It is the front part of the knee when the kneec is exposed to damage, then it must be replaced to maintain the movement of the knee and the success rate of this operation is relative. Therefore, it is preferable to replace the knee completely when the kneecap is damaged.
Total complex knee replacement: Here the artificial joint that is damaged will be replaced by another new joint and this procedure is performed upon exposure to severe inflammation of the knee joint or when more than one operation is performed to replace the knee joint.
Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction:
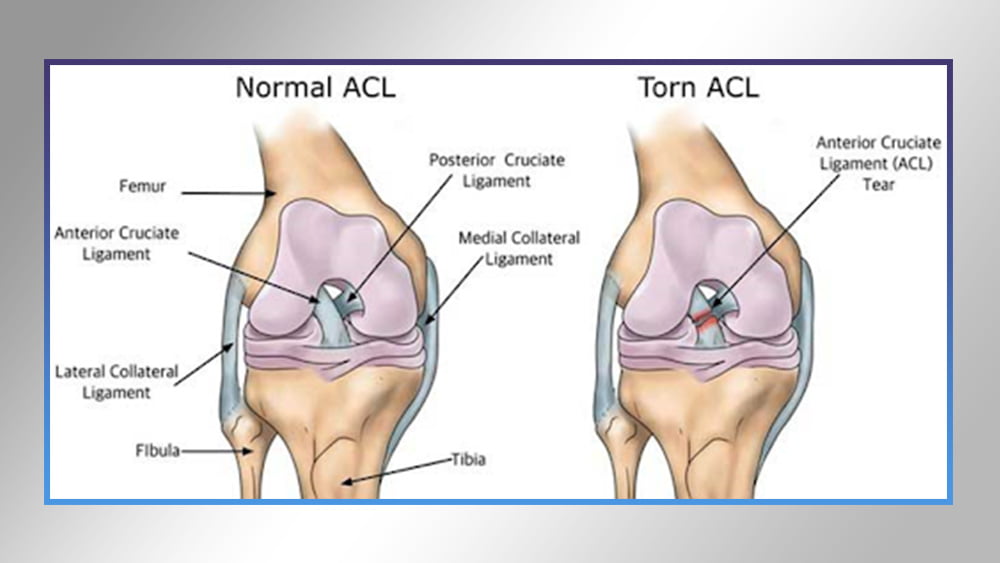
The anterior cruciate ligament restoration process aims to restore the stability and strength of the knee joint after the original ligament has been torn, the worn ligament is removed and replaced by another from a square body or an artificial ligament and the stability of the knee joint is of four ligaments (based on linking the thigh and leg bones together) :
Anterior cruciate ligament
• medial lateral ligament
Lateral lateral ligament
Posterior cruciate ligament
The importance of the anterior cruciate ligament is important because it in turn preserves the leg from sliding in front of the femur and provides stability as well when the knee rotates.
Anterior cruciate ligament injuries:
The injuries in the anterior cruciate ligament are among the most prevalent here, especially for sports and movement players.
How is the restoration of Rabat done?
An incision is made in the front of the knee to insert surgical tools such as the scope, as well, to allow the medical team to see a clear inside the knee during the operation.
Then the frayed anterior cruciate ligament is removed and the area cleaned, after which holes in the leg and thigh bone are made to fix the new ligament, and then the ligament and knee movement is well tested and the extent of stability.
Congenital anomalies in children:
Children can be born and have some defects and abnormalities in the bone and be hereditary or as a result of infections and others, or fractures.
Congenital anomalies are in the bone since the first day of birth, for example a lack of fingertips or shortness in the upper or lower limb, and it may also be unclear defects such as congenital or genetic dislocation, and if these defects are not discovered early, it will be difficult to treat them later.
treatment :
Before surgery:
Tests are performed using the child’s MRI and X-rays and analyzes are carried out. According to these reports, a treatment plan is established for the child patient.
Operation and qualification:
The child can be infected with “clubfoot” disease, then surgery must be done in stages according to the child’s condition and be between 6 and 9 months of the child’s age in order for the man to be positioned in a greater position and the sick child is in a better health condition so that the treatment is complete. Say that the child starts walking and be the first A proper move for him.
The foot and ankle are normally positioned to the normal position by making elongation of the evacuated tendon, loosening the muscles, opening the ankle and foot joints to re-position the foot bones well and fixing by a metal skewer and the splint is placed for a period of two weeks then the stitches are removed and the foot position is repaired to the best position and return We put it in gypsum for 1 month and the cast is changed and remains for a month and a half, and we remove the metal skewer after about a month and a half of the process.